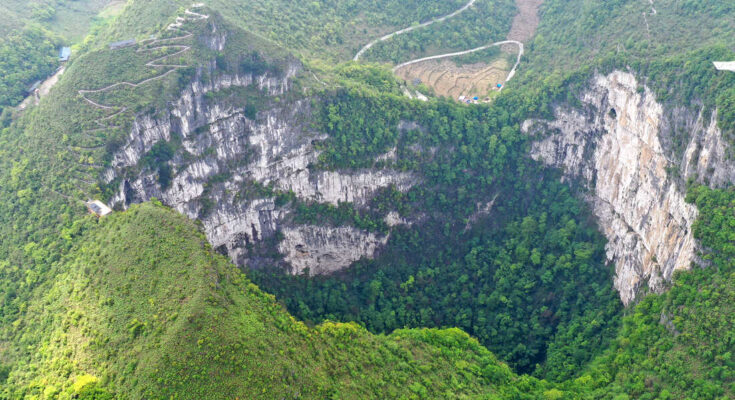
In a remarkable geological discovery, scientists have uncovered a massive sinkhole in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China, featuring a lush underground forest that could be home to undiscovered species. This natural wonder, classified as a tiankeng or “heavenly pit,” underscores the region’s geological richness and ecological significance.

Dimensions and Geological Features
The newly discovered sinkhole is colossal in scale, measuring approximately 630 feet (192 meters) in depth, 1,004 feet (306 meters) in length, and 492 feet (150 meters) in width. The sheer size of this chasm places it among the largest known sinkholes in the world. At its base lies a vibrant forest ecosystem, where ancient trees tower up to 131 feet (40 meters) high, their branches stretching toward the limited sunlight filtering through the opening above. The dense undergrowth reaches shoulder height, providing a habitat that is both mysterious and potentially teeming with undiscovered life.

Formation and Scientific Significance

Sinkholes like this form as a result of the slow and persistent dissolution of limestone and other soluble rock types by acidic rainwater. Over thousands or even millions of years, water seeps into the bedrock, carving out vast underground caves and caverns. Eventually, when the support structures weaken, the ground above collapses, exposing a hidden subterranean world. This process, known as karst formation, is responsible for some of the most breathtaking landscapes on Earth.
Karst topographies, such as those found in Guangxi, are not only visually stunning but also environmentally critical. They function as conduits for aquifers, supplying fresh water to an estimated 700 million people worldwide. These sinkholes also serve as isolated ecosystems where species can evolve in unique ways, shielded from external influences for thousands of years.
Biodiversity and Ecological Importance
The discovery of an untouched forest within the sinkhole raises exciting possibilities for biodiversity research. Scientists speculate that this secluded environment could harbor species yet to be documented, much like other sinkholes around the world that have revealed new plants, insects, and even amphibians. The towering trees and dense vegetation suggest a self-sustaining ecosystem, possibly home to unique flora and fauna that have adapted to the limited light and specific microclimate conditions.
Given the depth and isolation of the sinkhole, researchers plan to conduct thorough biological surveys to document any previously unknown organisms. Such findings could provide valuable insights into evolutionary biology, conservation efforts, and the resilience of life in extreme environments.
The Region’s Geological Heritage
Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region is renowned for its extraordinary karst landscapes, many of which are recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites. This latest discovery brings the total number of known sinkholes in Leye County alone to 30, further cementing the area’s reputation as a geological hotspot. The region attracts scientists, speleologists, and nature enthusiasts from around the world, drawn by its dramatic limestone formations, underground rivers, and unique cave ecosystems.
A Window into Earth’s Hidden Wonders
This newly uncovered “heavenly pit” serves as a reminder of the Earth’s uncharted mysteries, where entire ecosystems can exist beyond the reach of human civilization. As exploration continues, researchers hope to gain a deeper understanding of these underground landscapes and the role they play in global biodiversity.
The discovery of this sinkhole in China is not just an awe-inspiring spectacle—it is a gateway to scientific inquiry, conservation awareness, and a testament to the natural world’s ability to surprise and inspire humanity.