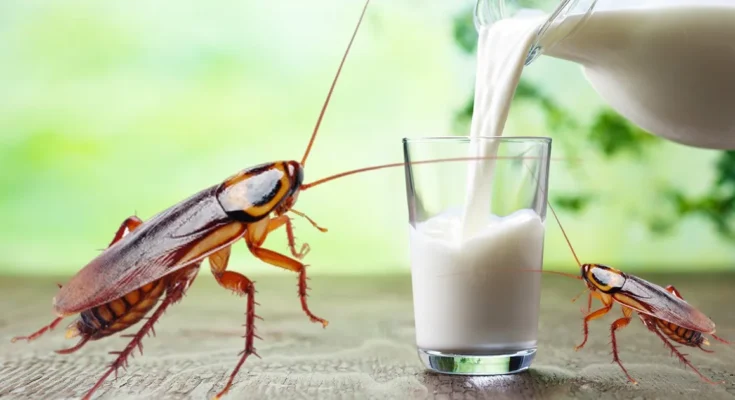
In the quest for sustainable and highly nutritious food sources, scientists have uncovered an unusual yet promising candidate: cockroach milk. Specifically, the milk-like substance produced by Diploptera punctata, a species of cockroach capable of giving birth to live young, has been found to be three times more nutritious than cow’s milk. This discovery has sparked intrigue in the scientific community, as researchers explore its potential benefits and methods for large-scale production.

What is Cockroach Milk?
Unlike traditional milk from mammals, cockroach milk is not liquid but rather a protein-rich crystalline substance. Diploptera punctata produces this nutrient-dense secretion to nourish its developing embryos. Scientists have found that this substance contains a well-balanced composition of proteins, fats, and sugars, making it an efficient energy source. Furthermore, it has all the essential amino acids required for human consumption, making it a complete food.
Nutritional Superiority
One of the most fascinating aspects of cockroach milk is its high caloric and nutritional density. Researchers have determined that the protein crystals in cockroach milk contain three times the energy content of an equivalent amount of cow’s milk. This means that even a small quantity of cockroach milk could provide significant nutrition, making it an attractive option for food security and sustainable nutrition.
Beyond its macronutrient composition, cockroach milk also contains essential lipids and carbohydrates, which contribute to its status as a well-rounded food. Additionally, studies suggest that the time-released proteins in cockroach milk allow for a slow and steady nutrient release, potentially improving digestion and nutrient absorption in humans.
The Potential Benefits for Human Consumption
With the world’s population steadily increasing and food resources becoming strained, alternative sources of nutrition are needed. Cockroach milk presents an interesting solution for several reasons:
- High Nutritional Value: Since it is a complete protein source with essential amino acids, it could serve as an alternative for those with dietary restrictions or as a supplement for populations facing malnutrition.
- Sustainability: Insect-based foods have been shown to have a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional livestock farming. Raising insects requires significantly less land, water, and feed than raising cows, sheep, or chickens, making cockroach milk an eco-friendly alternative.
- Long-Term Energy Release: The slow digestion of cockroach milk proteins means that it could be useful for endurance athletes or individuals needing sustained energy throughout the day.
- Potential Medical Applications: Some researchers suggest that cockroach milk might have bioactive properties that could benefit gut health, immunity, or metabolic function.
Challenges to Production and Consumption
Despite its promising nutritional benefits, several obstacles need to be addressed before cockroach milk can become a viable food source for humans:
- Production Scale: Extracting milk from individual cockroaches is neither practical nor efficient for large-scale production. Scientists are currently exploring ways to replicate the protein crystals synthetically using biotechnological methods, such as yeast fermentation or genetic engineering.
- Cultural Acceptance: The idea of consuming a product derived from cockroaches may be unappealing to many. Overcoming this psychological barrier would require strong marketing efforts, education, and possible incorporation into more familiar food products.
- Regulatory Approval: Before being introduced to the market, cockroach milk must undergo rigorous testing to ensure its safety for human consumption.
Future Prospects
As research continues, scientists are optimistic about the future of cockroach milk as a superfood. Advances in biotechnology may enable scalable production methods, making it more accessible to consumers worldwide. If properly marketed and integrated into existing dietary habits, cockroach milk could become a valuable nutritional resource, especially in regions where protein deficiencies are prevalent.
While the idea of consuming cockroach-derived food might seem unconventional, history has shown that dietary norms evolve. With the growing need for sustainable and nutritious food sources, cockroach milk could one day become a mainstream dietary supplement, contributing to global food security and nutritional health.
In the ever-changing landscape of food science, what may seem unusual today could be the staple of tomorrow. Cockroach milk, with its superior nutritional profile and potential sustainability, stands as a fascinating contender in the search for future superfoods.