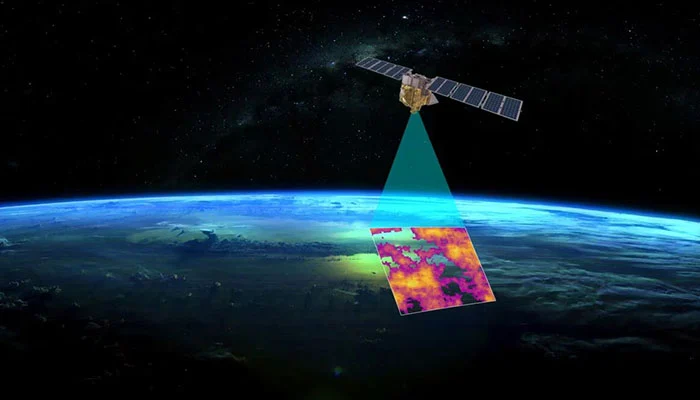
Google has taken a major step forward in environmental monitoring by launching its first satellite dedicated to early wildfire detection. This initiative is part of the FireSat constellation, a collaborative project involving Google, the Earth Fire Alliance, and Muon Space. The goal is to enhance global wildfire detection and response capabilities, using cutting-edge technology to monitor and mitigate fire-related disasters more effectively.

The inaugural FireSat satellite was launched on March 14, 2025, from California’s Vandenberg Space Force Base aboard SpaceX’s Transporter-13 mission. This launch marks the beginning of an ambitious plan to deploy over 50 satellites into orbit. These satellites are designed to detect wildfires at an early stage, identifying fires as small as 5×5 meters—approximately the size of a classroom. The advanced capabilities of the FireSat constellation are expected to revolutionize how wildfires are detected and managed worldwide.

Wildfires have become an increasing global concern due to climate change, rising temperatures, and prolonged drought conditions. Traditional detection methods rely heavily on ground reports, satellite imagery with delayed updates, and airborne surveillance, which can sometimes take hours or even days to confirm the presence of a fire. The FireSat system addresses these limitations by providing near-instantaneous data using a network of high-tech satellites equipped with state-of-the-art infrared sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms.

The FireSat satellites leverage advanced infrared technology to distinguish actual wildfires from other heat sources, such as industrial activity or controlled burns. This capability significantly reduces false alarms and ensures emergency responders receive accurate and timely data. The system is designed to provide global updates on fire activity every 20 minutes, offering real-time insights that can aid in faster decision-making and deployment of firefighting resources.

The need for improved wildfire detection has never been greater. In recent years, devastating wildfires have caused widespread destruction across various regions, including the United States, Canada, Australia, and Europe. These fires have not only resulted in massive property losses but have also led to severe environmental damage, habitat destruction, and loss of human lives. The FireSat project aims to mitigate these impacts by providing a proactive approach to wildfire management.
With the full FireSat constellation expected to be operational by 2030, the system will offer continuous wildfire monitoring and rapid detection capabilities. By integrating real-time satellite data with AI-driven analytics, the FireSat network will help emergency services and government agencies coordinate more efficient firefighting strategies. The ability to pinpoint small fires before they escalate into large-scale disasters will be a game-changer in wildfire prevention and response efforts.

Moreover, the data collected by FireSat will be invaluable for researchers studying wildfire patterns, climate change, and environmental shifts. The insights gained from this satellite network will contribute to long-term strategies for fire prevention, forest management, and climate adaptation.
Beyond immediate wildfire response, FireSat’s technology has broader implications for disaster management and environmental monitoring. The same infrared sensing capabilities can potentially be adapted to track other natural disasters, such as volcanic eruptions, industrial explosions, and methane leaks. This multi-functional approach could enhance global efforts to monitor and mitigate environmental hazards.
Google’s involvement in this initiative underscores the increasing role of technology companies in addressing climate-related challenges. By collaborating with organizations like the Earth Fire Alliance and Muon Space, Google is leveraging its expertise in AI, data processing, and cloud computing to drive meaningful advancements in disaster response and environmental protection. This initiative aligns with Google’s broader commitment to sustainability and its ongoing efforts to develop technological solutions for global challenges.
As FireSat’s deployment progresses, the world will witness a transformative shift in how wildfires are detected, monitored, and managed. By harnessing the power of space-based technology, AI, and collaborative partnerships, this project has the potential to save lives, protect ecosystems, and reduce the economic impact of wildfires.
In the coming years, as the FireSat network expands, emergency responders, policymakers, and environmental organizations will have a powerful new tool at their disposal—one that provides real-time insights into fire activity, enabling faster, smarter, and more effective wildfire response strategies. This pioneering effort represents a significant milestone in the ongoing battle against wildfires and their devastating effects on communities and the planet.