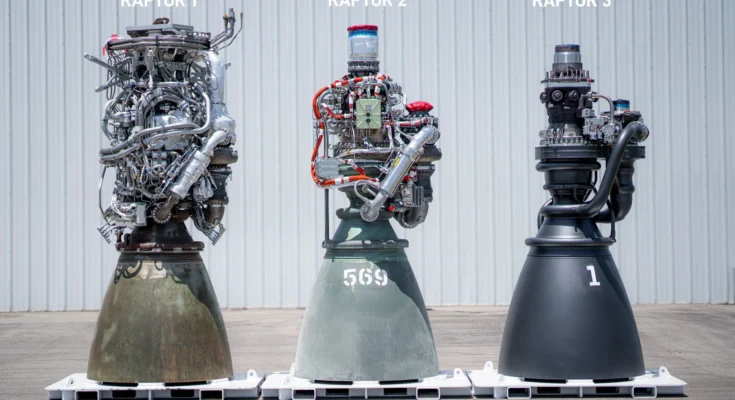
SpaceX’s Raptor engine stands as one of the most advanced rocket engines ever developed, marking a significant step forward in humanity’s journey to space exploration. Designed for the company’s ambitious Starship program, the Raptor has undergone remarkable improvements since its inception. From Raptor 1 to Raptor 2, and now the anticipated Raptor 3, SpaceX has consistently pushed the boundaries of propulsion technology, bringing us closer to interplanetary travel.

The Origins of the Raptor Engine
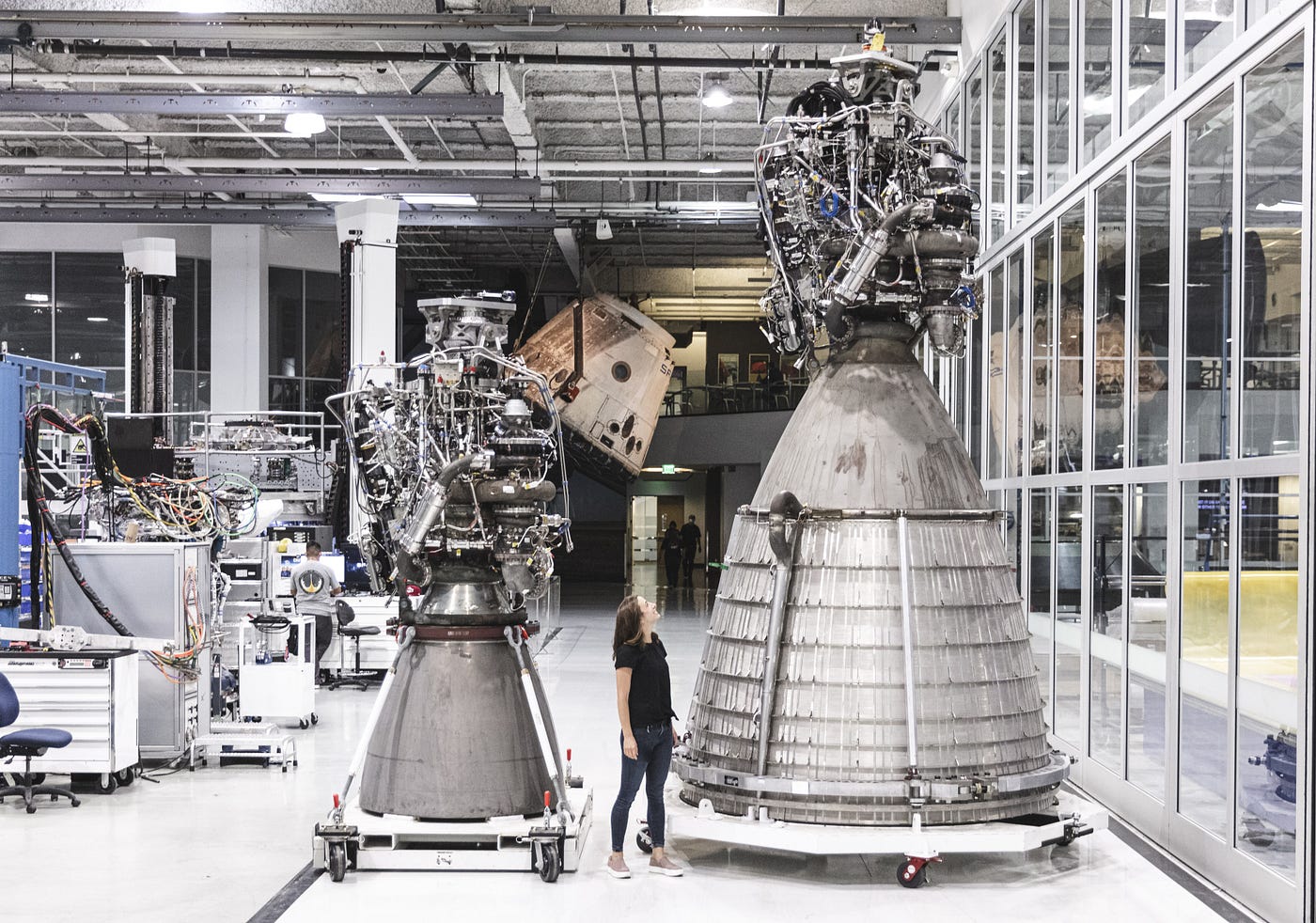
SpaceX began working on the Raptor engine in the early 2010s with the vision of creating a fully reusable, highly efficient propulsion system. Unlike the Merlin engines used on the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets, the Raptor is a full-flow staged combustion engine running on liquid methane and liquid oxygen (Methalox). This choice of fuel enhances efficiency and enables easier refueling on Mars, a key factor in Elon Musk’s long-term vision of making life multiplanetary.
Raptor 1: The First Iteration

The first generation of the Raptor engine was a technological breakthrough, but it came with complexities. Capable of generating approximately 185 tons of thrust, Raptor 1 featured a highly intricate design. While it demonstrated the potential of full-flow staged combustion, the engine proved challenging to manufacture and maintain. SpaceX rapidly iterated on the design, learning from extensive test firings at their facilities in Texas.
Raptor 2: A Major Step Forward

In response to the manufacturing challenges of Raptor 1, SpaceX introduced Raptor 2, a more powerful and simplified version. With an increased thrust output of approximately 230 tons, Raptor 2 delivered improved reliability while reducing production costs. The redesign focused on fewer parts, improved combustion stability, and better cooling mechanisms. These improvements allowed SpaceX to conduct more frequent and efficient static fire tests, accelerating the development of the Starship system.
One of the major upgrades in Raptor 2 was the ability to operate under extreme conditions with greater efficiency. The engine’s simpler design meant that it was more robust and easier to mass-produce, a critical factor in building a fleet of Starships capable of carrying cargo and passengers to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Raptor 3 and the Future of Space Travel

As SpaceX continues to refine its propulsion technology, Raptor 3 is expected to push the boundaries even further. While details remain scarce, early reports suggest that the new version will feature even greater thrust, improved thermal performance, and a further reduction in manufacturing complexity. With each iteration, SpaceX is moving closer to making Starship a reality—a fully reusable rocket capable of interplanetary travel.
Conclusion
The evolution of the Raptor engine showcases SpaceX’s relentless pursuit of innovation. From Raptor 1 to Raptor 2 and the upcoming Raptor 3, each advancement brings us closer to the dream of deep space exploration. With Starship set to revolutionize space travel, the Raptor engine remains at the heart of this bold endeavor, proving that the future of humanity in space is closer than ever before.