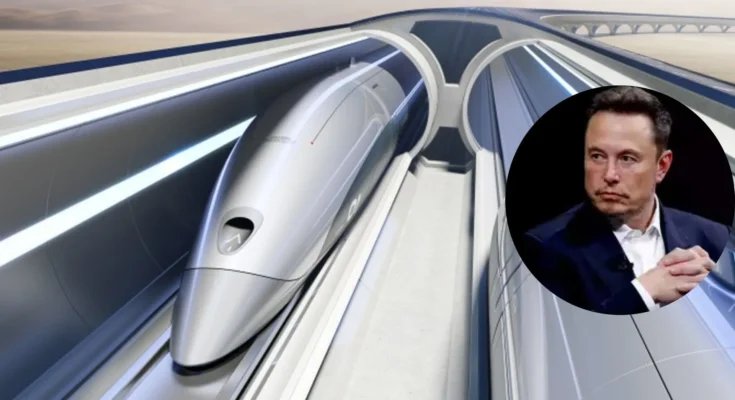
In December 2024, Elon Musk, the CEO of The Boring Company, reignited discussions about a transatlantic tunnel connecting New York City and London. Responding to online discussions about a proposed $20 trillion tunnel that could facilitate 54-minute travel between the two cities, Musk claimed that his company could accomplish the project for $20 billion—1,000 times less than the initial estimate.

The concept of a transatlantic tunnel is not new; it has been a subject of fascination for over a century. Early proposals envisioned a submerged floating tunnel or a tunnel beneath the ocean floor, utilizing advanced technologies to achieve unprecedented travel speeds. In the early 2000s, researchers at MIT proposed a magnetic levitation (maglev) train line that would span approximately 3,500 miles between New York and London, potentially reaching speeds up to 1,200 miles per hour. However, the estimated cost for such a project was between $88 billion and $175 billion at that time.
Musk’s proposal centers around Hyperloop technology, a high-speed transportation system he conceptualized in a 2013 white paper. The Hyperloop involves pressurized pods traveling through near-vacuum tubes, significantly reducing air resistance and enabling speeds exceeding 600 miles per hour. The Boring Company has been developing this technology, with plans for routes such as Washington, D.C., to New York City, which could potentially reduce travel time to under 30 minutes.
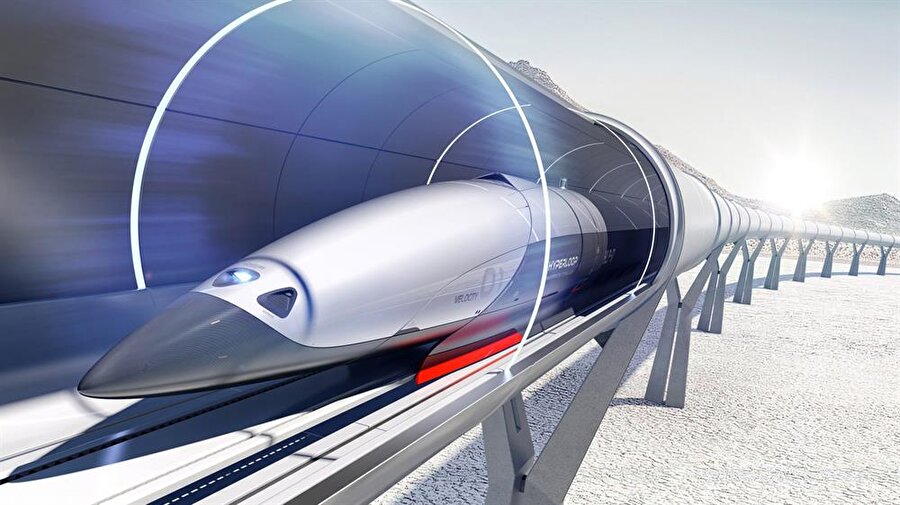

Despite the ambitious vision, several significant challenges persist:
- Technical Feasibility: Constructing a tunnel spanning over 3,000 miles beneath the Atlantic Ocean presents unprecedented engineering challenges. The structure would need to withstand immense oceanic pressure, seismic activity, and corrosion, requiring materials and construction techniques that are either in developmental stages or yet to be invented.
- Financial Viability: Even with Musk’s assertion of a $20 billion budget, experts question the accuracy of this estimate. Historical infrastructure projects, such as the Channel Tunnel connecting the UK and France, experienced significant cost overruns despite being of much smaller scale. The financial risks associated with a transatlantic tunnel are substantial, and securing investment would be a formidable task.
- Regulatory and Environmental Concerns: A project of this magnitude would require extensive regulatory approvals from multiple governments and international bodies. Environmental impact assessments would need to address potential disruptions to marine ecosystems, both during construction and operation. The legal and bureaucratic complexities could lead to prolonged delays and increased costs.
Moreover, while Hyperloop technology has shown promise in controlled environments, it remains largely unproven at the scale required for transatlantic travel. The longest Hyperloop test to date involved a pod traveling 11.8 kilometers at a speed of 25 miles per hour in Switzerland, far below the speeds and distances required for a transoceanic journey.

Public and expert reactions to Musk’s proposal have been mixed. Proponents argue that, if realized, the transatlantic tunnel could revolutionize global travel, significantly reducing transit times and fostering economic integration. Critics, however, highlight the myriad technical, financial, and regulatory hurdles that render the project highly speculative at this stage.
In summary, while Elon Musk’s vision of a $20 billion transatlantic tunnel leveraging Hyperloop technology is intriguing and has sparked renewed interest in futuristic transportation solutions, the practical implementation of such a project faces monumental challenges. Advancements in engineering, materials science, and international cooperation would be essential to transform this ambitious concept into reality.